The use of technology in the medical field has brought about big changes, from advanced surgical methods to innovative diagnostic tools. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are two technologies that have made their way into medical training. They offer immersive and interactive experiences for healthcare professionals. In this detailed exploration, we will look at how AR vs VR are used in medical training and how they can enhance learning, improve patient outcomes, and shape the future of healthcare education.
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Before we dive into how they’re used in medical training, let’s understand the basics of AR and VR:
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR adds digital elements to what we see in the real world. It can be used on devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR headsets. AR lets us interact with digital stuff while we’re aware of the real world around us.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR, on the other hand, immerses us in a completely digital world. It usually needs VR headsets that cover our field of vision, making us feel like we’re in a different place. VR can be entirely computer-made or a 360-degree video of a real place.



Applications of AR vs VR in Medical Training
Learning Human Anatomy:
Understanding the human body is crucial in medical training. AR and VR have transformed anatomy education by offering interactive and immersive learning experiences.
-
- VR Anatomy Apps: Medical students can explore 3D models of the human body in VR. They can move them around, dissect them, and examine body parts from different angles, helping them understand complex spatial relationships.
- AR Anatomy Cards: AR cards have anatomical pictures. Scanning them with a smartphone or tablet reveals 3D models of organs, bones, or systems. This hands-on approach makes it easier to remember and understand.
Surgical Training:
Learning surgery usually involves a “watch one, do one, teach one” approach. AR and VR are changing this by offering safe and repeatable training.
-
- VR Surgical Simulations: VR provides a realistic surgical setup where trainees can practice procedures without the risk of real surgery. It helps improve their skills, decision-making, and understanding of space.
- AR Surgical Navigation: Surgeons use AR headsets to see real-time data and images during surgery. This tech boosts accuracy and reduces the chance of problems.
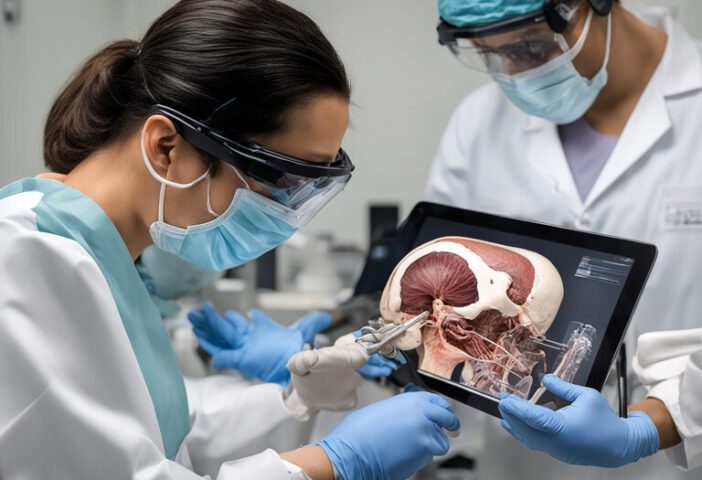
Patient Interaction:
Medical professionals must communicate well with patients. AR and VR can help build empathy, improve patient interactions, and enhance the patient experience.
-
- VR Empathy Training: VR puts medical students in patients’ shoes, helping them understand the emotional and physical aspects of various medical conditions.
- AR Language Translation: AR apps can translate spoken words in real time, allowing healthcare providers to communicate effectively with patients who speak different languages.
Diagnostic Skills:
Diagnostic skills are vital for healthcare professionals. AR and VR offer innovative ways to hone these skills.
-
- VR Medical Imaging: Trainees can explore 3D versions of medical images, such as MRI and CT scans, to improve their ability to spot problems and make accurate diagnoses.
- AR Diagnostic Challenges: AR apps overlay diagnostic challenges on real-life scenarios. This helps medical students practice diagnosing conditions under different conditions and patient presentations.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy:
AR and VR are not just for learning. They’re also used for rehab and physical therapy.
-
- VR Rehabilitation Games: Patients can play VR games designed for rehab, like games that help improve movement and coordination after an injury or surgery.
- AR Exercise Guidance: AR apps offer real-time guidance during physical therapy sessions, helping patients do exercises the right way.
Mental Health Training:
AR and VR can be used for mental health training, helping healthcare providers understand and treat various mental health conditions.
-
- VR Exposure Therapy: VR can simulate situations related to mental health conditions, allowing therapists and patients to confront and manage specific fears and anxieties.
- AR Social Interaction Simulations: AR apps create social situations that help people with social anxiety practice and improve their social skills.
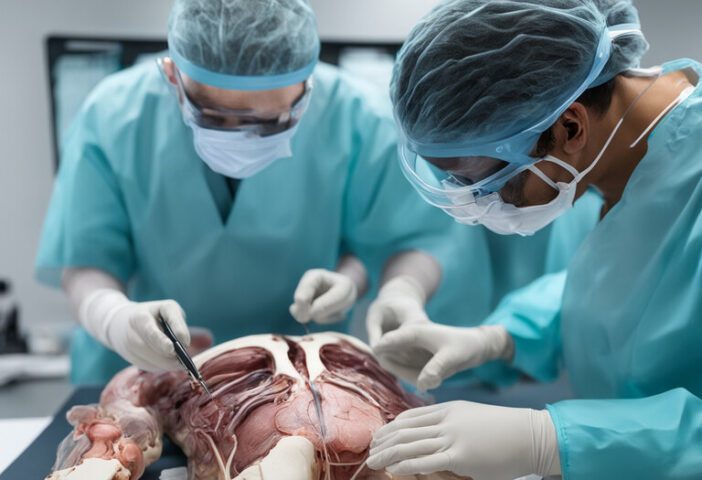
Global Medical Collaboration:
AR and VR can connect healthcare professionals worldwide, promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing.
-
- VR Medical Conferences: VR is used to host medical conferences and seminars, providing a platform for experts from around the world to present their research and innovations.
- AR Consultations: Healthcare providers can use AR headsets for remote consultations. This way, specialists from different places can work together on complex cases.
Advantages of AR vs VR in Medical Training
- Safety: AR and VR simulations offer a safe environment for trainees to learn and practice without real patients being in danger. This is especially important for surgical training.
- Immersive Learning: Immersion increases engagement and retention. Medical trainees can “experience” medical conditions and procedures, helping them understand better.
- Repeatability: Trainees can repeat simulations as many times as needed, which helps them master skills and procedures before they work with real patients.
- Interactivity: AR and VR are interactive, allowing users to interact with 3D models, do virtual procedures, and engage actively with the content.
- Global Collaboration: These technologies help healthcare professionals from all over the world collaborate, share knowledge, and exchange expertise.
- Patient Empathy: VR experiences help healthcare providers understand the patient’s point of view, which ultimately improves patient care.
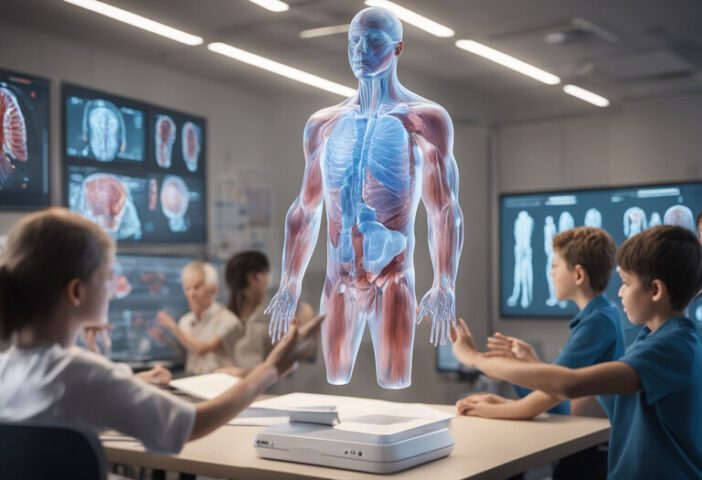
Challenges and Considerations
While AR and VR have great potential in medical training, they also come with their own challenges and things to think about:
- Cost: High-quality AR and VR equipment can be expensive. Making sure all medical training institutions can access these technologies is a challenge.
- Content Quality: Creating accurate and effective AR and VR medical content takes expertise and resources. Low-quality content can make learning less effective.
- Motion Sickness: Some users might get motion sickness when using VR, which can limit how long they can train.
- Integration: Putting AR and VR into existing medical education and healthcare systems needs planning and might face resistance.
- Privacy and Security: Patient data privacy and cybersecurity are important, especially in AR and VR systems used for remote consultations and data sharing.
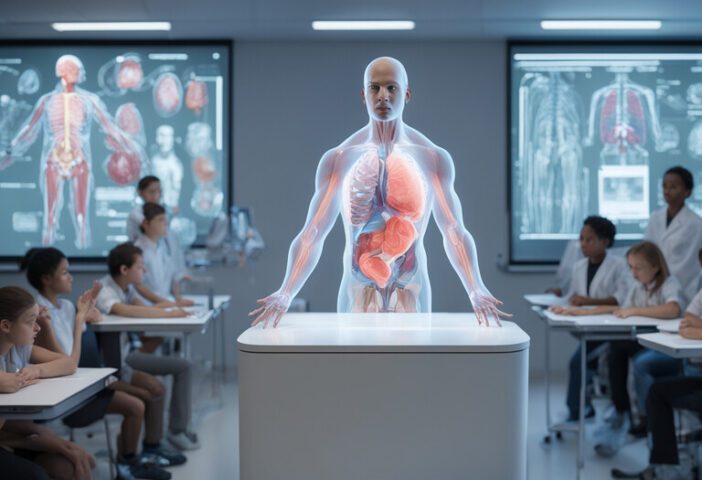
The Future of AR vs VR in Medical Training
The future of AR and VR in medical training is bright. These technologies are likely to play an even bigger role in healthcare education and patient care. Here’s what we can expect:
- Wider Adoption: As costs come down and content quality goes up, more medical institutions will adopt AR and VR in their training programs.
- Personalized Learning: AR and VR can be tailored to individual learning needs, helping students and professionals focus on areas where they need more practice.
- Advanced Simulations: Simulations will become even more realistic and versatile. Trainees will be able to practice a wider range of procedures in a risk-free environment.
- Continuing Education: AR and VR will be used for continuous professional development, helping healthcare providers stay up to date with the latest advances in medicine.
- Remote Learning: Especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, remote learning and virtual training have become more popular. AR and VR will continue to support remote learning and collaborations.
- Research Opportunities: AR and VR generate a wealth of data on how medical professionals learn and make decisions. This data can be used to improve training programs and medical practices.



Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are transforming medical training. They offer immersive, interactive, and safe learning experiences. From anatomy and surgery to patient interaction and mental health training, AR and VR have diverse applications in healthcare education. Although they come with challenges like cost and content quality, the future of AR and VR in medical training is promising.
As these technologies become more accessible and content improves, they will play a more significant role in medical education and patient care. The future holds personalized learning, advanced simulations, and opportunities for remote collaboration and research, ultimately leading to better-trained healthcare professionals and improved patient outcomes.































Your blog is quite impressive; it loads quickly as well. Could you kindly provide the affiliate link to the host where your site is hosted? I wish my own website could load as quickly as yours.
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly posts I might state That is the very first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to create this particular put up amazing Excellent job
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here regularly. I am quite certain I will learn lots of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!